随着产品精度和品质的提升,质检的难度和成本也随之增加,催生了许多检测方法。那么,您熟悉哪一种检测方式呢?是超声波、磁粉、渗透检测,还是人工目视检查?今天,我们将一起探讨一种重要的检测技术——X-Ray。With the improvement of product precision and quality, the difficulty and cost of quality inspection have also increased, giving rise to many detection methods. Which testing method are you familiar with? Is it ultrasonic, magnetic particle, penetration testing, or manual visual inspection? Today, we will explore an important testing technology together - X-Ray.
X-Ray(X光)X-Ray
提到X光,你可能会想到医生的诊室吧?其实在20世纪70年代初,X光主要是用来做医疗检查的。不过,随着工业上无损检测技术的发展,X光也逐渐进入了工业领域,成为提高产品质量的重要帮手。When mentioning X-rays, you might think of a doctor's office, right? In fact, in the early 1970s, X-rays were mainly used for medical examinations. However, with the development of non-destructive testing technology in industry, X-rays have gradually entered the industrial field and become an important helper in improving product quality.
01 什么是X-Ray01 What is X-Ray
X-Ray是一种看不见的电磁波,它能穿透很多材料,通过不同材料的密度和厚度来帮助我们查看物体内部的细节。通过X-Ray技术,我们可以生成二维或三维图像,这样就能发现产品内部的缺陷,比如裂纹和气泡等问题,确保一切正常运作。X-Ray is an invisible electromagnetic wave that can penetrate many materials, helping us see details inside objects through the density and thickness of different materials. Through X-Ray technology, we can generate 2D or 3D images, which allows us to detect internal defects in products, such as cracks and bubbles, ensuring everything functions properly.
02 X-Ray的二维成像与三维成像02 2D and 3D Imaging of X-Ray
二维成像2D Imaging
X射线二维成像是一种利用X射线穿透物体来查看其内部切面的方法。简单来说,X射线会穿过物体,然后记录下射线强度的变化,这样我们就能了解物体内部的情况。可以把X射线想象成一把"透视枪",当它对着一个神秘的箱子发射时,箱子后面的接收板会记录下射线穿透箱子后的强度变化。根据这些变化,我们可以绘制出箱子的内部横切面图。X-ray 2D imaging is a method that uses X-rays to penetrate objects and view their internal cross-sections. Simply put, X-rays pass through the object, and then changes in ray intensity are recorded, allowing us to understand the internal conditions of the object. X-rays can be imagined as a "perspective gun": when it fires at a mysterious box, a receiving plate behind the box records changes in the intensity of the rays after they penetrate the box. Based on these changes, we can draw a cross-sectional view of the interior of the box.
在这个过程中,X射线有两种主要的扫描方式。In this process, there are two main scanning methods for X-rays.
一种叫"平行束"One is called "parallel beam"
就像用手电筒直接照射一样Like shining a flashlight directly
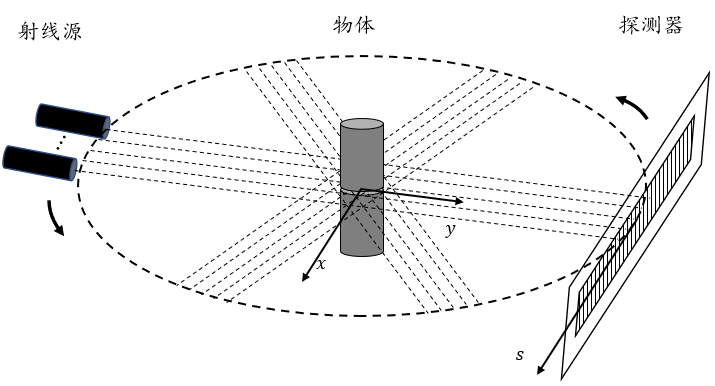
另一种是"扇形束"The other is "fan beam"
就像用扇形的灯光照亮箱子的一个平面Like illuminating a plane of the box with fan-shaped light
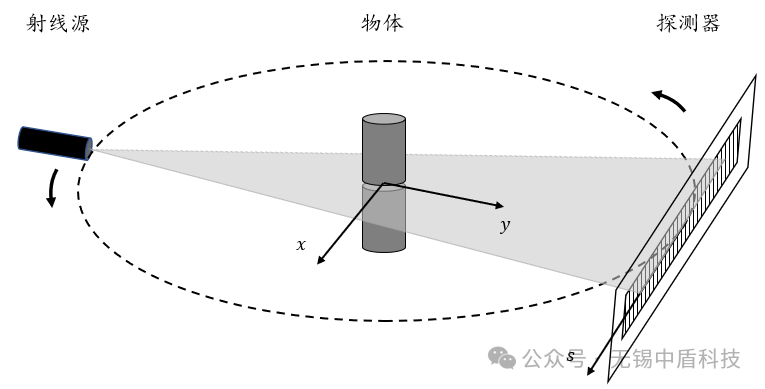
无论用哪种方式,X射线和接收板都会围绕着箱子转动,从不同角度拍照,最后把这些图像拼接成一幅完整的平面图。Regardless of which method is used, the X-ray and receiving plate will rotate around the box, taking photos from different angles, and finally splicing these images into a complete flat image.
这种方法可以用来检查焊接质量,发现微小裂纹和其他缺陷,速度快、成本低。不过,它只能提供一个平面的视图,这可能会影响我们准确识别缺陷的能力。This method can be used to check welding quality, detect micro-cracks and other defects, and is fast and low-cost. However, it can only provide a flat view, which may affect our ability to accurately identify defects.
三维成像3D Imaging
如果您想知道箱子内部的全貌,而不仅仅是一个切面,该怎么办呢?这时就需要三维成像了。X射线三维成像最常用的扫描方式是锥形束扫描。What if you want to see the full picture of the inside of the box, not just a single cross-section? Then you need 3D imaging. The most commonly used scanning method for X-ray 3D imaging is cone beam scanning.
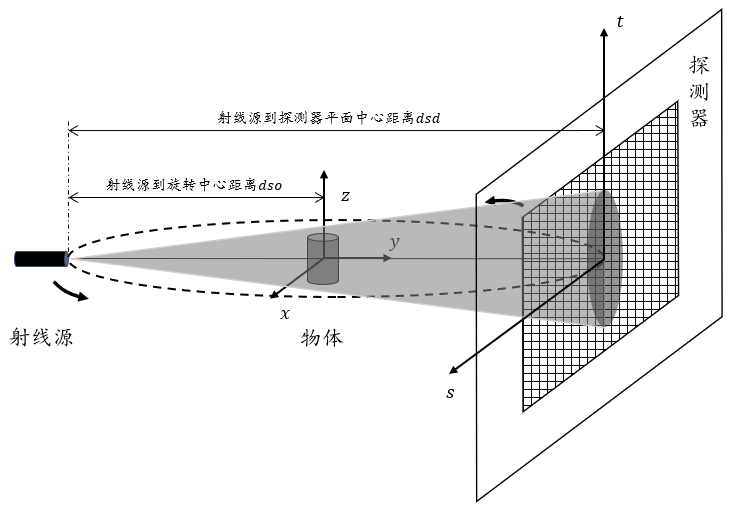
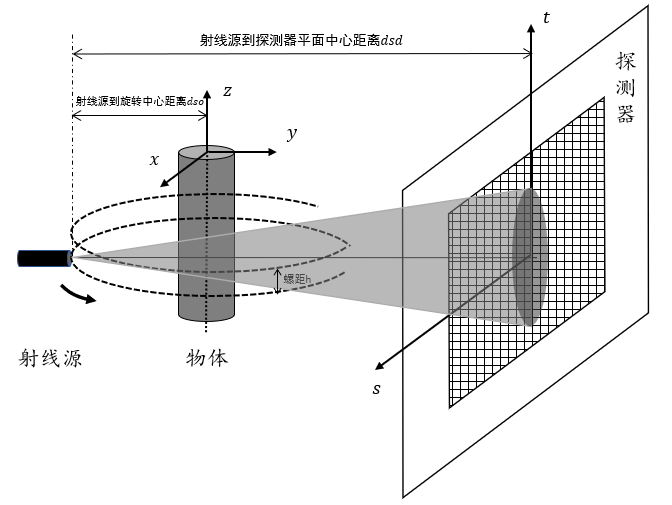
在这种方式中,X射线源会发射出呈锥形分布的射线,覆盖一个立体区域,它就像一个喷水喷头,从一个点向四面八方射出射线。接着,透视枪和接收板会一起围绕箱子旋转,从不同角度收集数据,最后将这些数据组合成一个立体的图像。这样一来,您就能清晰地看到箱子里究竟长什么样了!In this method, the X-ray source emits rays distributed in a cone shape, covering a three-dimensional area. It's like a water sprinkler head that shoots rays in all directions from one point. Then, the perspective gun and receiving plate rotate around the box together, collecting data from different angles, and finally combining this data into a three-dimensional image. This way, you can clearly see what's inside the box!
03 X-Ray在工业质检中的应用03 Applications of X-Ray in Industrial Quality Inspection
X-Ray成像可以用来无损地检测工业产品,适用范围从几微米的小物体到几米的大物体。它在工业质检中有着广泛的应用:X-Ray imaging can be used for non-destructive testing of industrial products, ranging from small objects of a few micrometers to large objects of several meters. It has a wide range of applications in industrial quality inspection:
- 泛半导体行业Pan-semiconductor industry
评估汽车电子IGBT、集成电路及其他电子元件的焊接质量等。Evaluating the welding quality of automotive electronics IGBT, integrated circuits and other electronic components.
- 汽车工业Automotive industry
检查汽车零部件(如发动机、齿轮箱和轮毂等)的内部结构。Inspecting internal structures of automotive parts (such as engines, gearboxes and wheels).
- 航空航天Aerospace
检测航空航天部件(如涡轮叶片、机翼和燃料管道)。Testing aerospace components (such as turbine blades, wings and fuel pipes).
- 铸造与焊接Casting and welding
查找铸件和焊接部件中的气孔、裂纹等缺陷。Finding defects such as porosity and cracks in castings and welded parts.
- 材料科学Material science
分析材料的微观结构,帮助研究新材料的特性。Analyzing the microstructure of materials to help research the properties of new materials.
- 新能源电池New energy batteries
检查锂电池的内部结构、极片对齐情况及气泡等问题。Checking the internal structure, pole piece alignment and bubbles of lithium batteries.
- 文物保护Cultural relics protection
无损检测文物的内部结构,帮助分析材质。Non-destructive testing of the internal structure of cultural relics to help analyze materials.
- 食品工业Food industry
检测食品中的异物和包装缺陷。Detecting foreign objects and packaging defects in food.
- 其他Others
X光技术还可以应用于多种其他领域,帮助提升质量检测的效果与效率。X-ray technology can also be applied to many other fields to help improve the effectiveness and efficiency of quality detection.
04 那比起其他检测方式,X-Ray有什么优势呢?04 What are the advantages of X-Ray compared to other testing methods?
无损检测:Non-destructive testing:
X-Ray可以在不接触和不破坏物体的情况下,检查内部的问题,并获取产品的二维和三维图像,这样既安全又高效。X-Ray can inspect internal problems without touching or damaging objects, and obtain 2D and 3D images of products, which is both safe and efficient.
高效快速:Efficient and fast:
与传统质检方法相比,X-Ray检测能快速检查多个部件,省时省力,提升生产效率。Compared with traditional quality inspection methods, X-Ray detection can quickly inspect multiple components, saving time and effort, and improving production efficiency.
精准可靠:Precise and reliable:
X-Ray技术能够清晰、准确地显示产品的内部缺陷,帮助工程师做出科学的决策。X-Ray technology can clearly and accurately display internal defects of products, helping engineers make scientific decisions.
ENDEND





